America isn’t making electrical energy the best way it did twenty years in the past.
How the US made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel surpassed coal because the nation’s prime supply of energy in 2016, and renewables like wind and photo voltaic have grown rapidly to change into main gamers within the U.S. energy system.
However each state has its personal story.
In Nevada, pure fuel grew to become the highest supply of electrical energy era in 2005, sooner than in lots of different locations. Extra just lately, solar energy has surged there.
Wind energy has taken off in Iowa over the previous twenty years, beating out coal in 2019 to change into the state’s largest supply of energy era.
Even in Wyoming, the place coal nonetheless dominates electrical energy era, various sources of energy have made regular positive aspects.
Fossil fuels nonetheless generate the vast majority of America’s electrical energy, however the shift from coal to pure fuel and renewable energy has helped reduce planet-warming carbon dioxide emissions and different dangerous air pollution.
Final yr, coal was the highest electrical energy gasoline in 10 states, down from almost two-thirds of states in 2001. Pure fuel largely took over throughout that point, however wind additionally emerged as a number one energy supply throughout the Midwest.
Supply: U.S. Power Info Administration
Nonetheless, specialists say there’s a lengthy technique to go if the nation desires to zero out emissions from the facility sector to struggle local weather change, a aim set by President Biden.
Switching from coal to fuel “will get you a part of the best way there,” stated Melissa Lott, a researcher on the Middle on International Power Coverage at Columbia College, as a result of burning pure fuel for energy produces fewer carbon dioxide emissions than burning coal. However fewer emissions just isn’t the identical as zero emissions, she added. “Many extra applied sciences, together with renewables, have to be constructed rapidly to get us all the best way to our local weather objectives,” Dr. Lott stated.
Mr. Biden’s signature local weather and vitality regulation, the 2022 Inflation Discount Act, aimed to turbocharge the expansion of renewable wind and photo voltaic vitality nationwide and to help different clear energy applied sciences like nuclear vitality, superior batteries and carbon seize and storage for fuel crops. However the way forward for that regulation remains uncertain in an election yr, with Republicans promising to repeal a lot of its clean-energy provisions.
What occurs on the federal degree is just a part of the equation. States have the facility to speed up, decelerate or block clear vitality, too.
We charted how electrical energy era has modified in each state to date, from 2001 to 2023, utilizing knowledge from the US Power Info Administration. Discover your state beneath:
How Alabama made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
In 2001, coal fueled greater than half of the electrical energy produced in Alabama, however most of the state’s getting older coal energy crops have closed since then or shifted to burning cheaper pure fuel. By 2014, fuel had change into the highest electrical energy supply within the state, adopted by nuclear. And, final yr, coal fueled simply 14 p.c of the state’s electrical energy era.
Hydro has lengthy been Alabama’s largest supply of renewable energy. The state produced lower than 1 p.c of its energy from photo voltaic vitality final yr.
Alabama generates extra electrical energy than it consumes and usually sends about one-third of its output to close by states. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Alaska made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel has been Alaska’s prime supply of energy for twenty years, offering greater than half of the state’s electrical energy in most years. Hydro, petroleum and coal provide many of the relaxation. In 2010, Alaska set a nonbinding goal to supply 50 p.c of its electrical energy from renewable and various vitality sources by 2025, however the state has solely seen a small uptick in wind energy era since then.
Alaska has its personal electrical grid, which implies “no matter electrical energy is created there’s what they’re consuming,” stated Glenn McGrath, an influence methods analyst on the U.S. Power Info Administration. “It’s about as remoted as you will get.”
Many rural communities in Alaska should not related to the primary grid and use diesel mills for energy, though smaller, community-based wind turbines have gotten extra widespread.
How Arizona made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was Arizona’s prime supply of electrical energy era till 2016, when pure fuel surpassed it. Coal-fired era has declined quickly over the previous decade as among the state’s coal energy crops shut down and others switched to cheaper pure fuel.
In recent times, pure fuel has taken over because the state’s prime supply of energy, with fuel fueling 46 p.c of Arizona’s electrical energy era final yr. The state can also be house to the second-largest nuclear energy plant within the nation.
Arizona makes extra electrical energy than it makes use of and exports energy to close by states. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
The state has ample photo voltaic assets. Its largest utility, Arizona Public Service, set a voluntary goal of getting 65 p.c of its electrical energy from carbon-free sources by 2030 and one hundred pc by 2050. Nonetheless, the utility lobbied against proposals to codify these renewable objectives into regulation.
How Arkansas made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was the most important supply of electrical energy era in Arkansas for a lot of the previous twenty years. However its position within the state’s electrical combine diminished over time as pure fuel energy expanded. After vying with coal for the highest slot, fuel has been the state’s largest supply of energy era since 2022.
Arkansas generates extra electrical energy than it consumes and sends energy to close by states. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How California made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel has been California’s prime electrical energy gasoline since 2001, however greater than half of the facility produced within the state final yr got here from renewable vitality and different carbon-free sources, together with photo voltaic, wind, geothermal, hydro and nuclear.
Solar energy, particularly, has grown quickly over the previous decade, largely due to supportive state insurance policies. On the similar time, nuclear energy has declined. (One of many state’s two nuclear crops closed in 2012. The opposite is now slated to retire in 2030.)
California has usually led the best way on clear energy, utilizing state coverage to encourage the adoption of fresh energy applied sciences like photo voltaic panels and giant grid batteries. In 2018, the state set a aim for utilities to get all of their electricity from zero-carbon sources by 2045. State utilities and regulators at the moment are wrestling with how rapidly they’ll scale back dependence on pure fuel whereas nonetheless sustaining a dependable energy provide.
California consumes extra electrical energy than it generates inside its borders and usually imports about one-third to one-fifth of the facility it makes use of. (Imports should not mirrored within the chart above.)
How Colorado made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal has been Colorado’s prime supply of electrical energy for greater than twenty years. However coal-fired era shrank to 32 p.c of the state’s energy combine final yr from 76 p.c in 2001. On the similar time, pure fuel and wind energy elevated their position within the state’s electrical combine. In recent times, wind generators have provided greater than 1 / 4 of the electrical energy produced in Colorado, sufficient to change into the state’s second-largest supply of electrical energy in 2021 and 2022. However fuel energy topped wind once more final yr.
Colorado goals to get 100 percent of its electricity from renewable sources by 2040. The state’s largest utility, Xcel Power, plans to phase out its remaining coal-burning power plants by 2030 in favor of cleaner options.
Colorado often consumes extra electrical energy than it generates and imports energy from close by states. (Imports should not proven within the chart above.)
How Connecticut made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel and nuclear vitality have fueled the overwhelming majority of Connecticut’s electrical energy era over the past twenty years. However fuel era has elevated considerably since 2010 and fuel now provides almost 60 p.c of the facility produced within the state.
On the similar time, the quantity of electrical energy that comes from different fossil fuels, together with coal and petroleum, has declined. Connecticut’s final remaining coal plant, Bridgeport Harbor, retired in 2021.
Connecticut goals to get 100 percent of its electricity from zero-emissions sources by 2040. Final yr, nuclear energy offered 33 p.c of the state’s electrical energy era and one other 5 p.c got here from renewable sources, largely photo voltaic.
How Delaware made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel displaced coal as the first supply of electrical energy produced in Delaware in 2010 and has dominated the state’s energy combine since then. Coal era, in the meantime, has dwindled. Coal fueled 70 p.c of the state’s energy era in 2008, its peak yr, however solely offered backup energy throughout some months final yr.
Partly due to this shift, carbon dioxide emissions from the state’s electrical energy sector have fallen over the previous decade. Delaware requires that state utilities generate or procure 40 percent of their electricity from renewable sources by 2035, together with 10 p.c from photo voltaic.
Energy produced in-state usually provides “a lot lower than the state wants,” in accordance with the U.S. Power Info Administration. Delaware will get the vast majority of its electrical energy from neighboring states by means of the regional grid. (Imports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Florida made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
In 2001, greater than one-third of the electrical energy produced in Florida got here from burning coal. Two years later, pure fuel surpassed coal because the state’s prime supply of energy era and has continued to develop its share within the state’s electrical combine ever since. By final yr, pure fuel fueled three-fourths of Florida’s electrical energy era, considerably greater than the nationwide common.
Regardless of its nickname, the Sunshine State has been slow to adopt solar power. However utility-scale photo voltaic installations have picked up in the last few years. Florida is the second-largest producer of electrical energy nationwide, after Texas, however nonetheless imports a small quantity of energy from neighboring states to satisfy shopper demand. (Imports should not mirrored within the chart above.)
In 2024, Florida lawmakers passed a bill that cuts help for renewable vitality initiatives and makes it simpler to construct pure fuel infrastructure. The brand new regulation prohibits building of offshore wind generators in state waters, repeals state grant applications that encourage vitality conservation and renewable vitality and cancels the state’s voluntary renewable vitality objectives.
How Georgia made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal offered the vast majority of Georgia’s electrical energy era by means of the 2000s however declined sharply throughout the 2010s as pure fuel energy elevated. Fuel has been the state’s prime supply of energy for many of the final decade, with nuclear energy usually in second place.
Georgia is the one state to carry new nuclear capability on-line in recent times: Two new reactors that opened in 2023 and 2024. They had been the primary new nuclear reactors within the nation to be constructed from scratch in a long time, however the initiatives had been tormented by delays and significant cost overruns.
Solar energy has additionally grown rapidly within the state in recent times, offering about 6 p.c of Georgia’s energy in 2023. The state can also be nonetheless increasing fossil gasoline energy. Georgia Energy, the state’s primary utility, plans to build a number of new producing stations fueled by oil and fuel within the coming years to serve growing power demand from knowledge facilities and new clean-energy manufacturing hubs.
How Hawaii made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Hawaii has relied closely on imported oil to make electrical energy for the previous twenty years. However the state has an ambitious plan to generate all of its energy from clear vitality sources by 2045. In September 2022, Hawaii shut down its final coal-burning energy plant, a significant milestone in direction of that aim. Final yr, there was no utility-scale coal era in Hawaii for the primary time for the reason that early Nineteen Seventies, however delays within the deployment of latest photo voltaic and battery initiatives meant oil-fired era ticked up.
The state just lately opened a new, large-scale battery storage facility as a part of its technique to switch the coal energy that was retired. (Battery charging and discharging just isn’t proven within the charts above, which replicate internet era.)
Photo voltaic era, largely from small-scale rooftop panels, has grown quickly within the state over the previous decade and offered almost 20 p.c of Hawaii’s energy final yr. In complete, about 31 p.c of the state’s electrical energy was made by renewable sources in 2023.
How Idaho made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Hydro generated the overwhelming majority of Idaho’s electrical energy throughout the 2000s and early 2010s. However in recent times, drought circumstances have pushed down the quantity of hydroelectric energy produced within the state. Idaho nonetheless makes the vast majority of its electrical energy from renewable sources, with hydro offering 43 p.c of in-state energy era final yr and wind and photo voltaic collectively offering one other 22 p.c. However pure fuel energy has expanded considerably on the similar time.
Idaho additionally imports a large quantity of energy from out of state to satisfy its electrical energy wants. Previously, a lot of this energy has come from coal-fired mills in neighboring states, however Oregon closed its last coal plant in 2020 and different close by coal crops are scheduled to close down over the subsequent a number of years. (Imports should not proven on the chart.)
How Illinois made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Nuclear vitality has been Illinois’s prime supply of energy era for a lot of the final twenty years, accounting for about half of the electrical energy produced within the state throughout most years. Coal was lengthy the second-largest energy supply, briefly surpassing nuclear as the highest era gasoline in 2004 and once more in 2008. However coal’s position within the state energy combine has declined considerably in recent times as older coal-fired energy crops have retired or been transformed to burn pure fuel. Each pure fuel and wind era have grown over the previous decade, and final yr fuel surpassed coal because the second-largest supply of energy within the state.
In 2021, Illinois set a aim of getting 100 of its energy from carbon-free vitality sources by 2050, however the state has struggled to meet shorter-term targets. Illinois produces significantly extra electrical energy than it makes use of and sends about one-fifth to Mid-Atlantic and Midwestern states by means of long-distance transmission strains. (Exports should not proven on the chart.)
How Indiana made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal fueled many of the electrical energy made in Indiana for greater than twenty years, however its share within the state’s energy combine has declined as pure fuel era has taken off and older coal-fired energy crops have retired. Final yr, fuel offered almost 40 p.c of the state’s electrical energy era, up from 2 p.c in 2001.
About 14 p.c of the state’s electrical energy got here from renewable sources final yr, largely wind. Over the previous decade, Indiana has used extra electrical energy annually than it produces inside its borders and imported the remainder from out of state. (Imports should not proven on the chart above.)
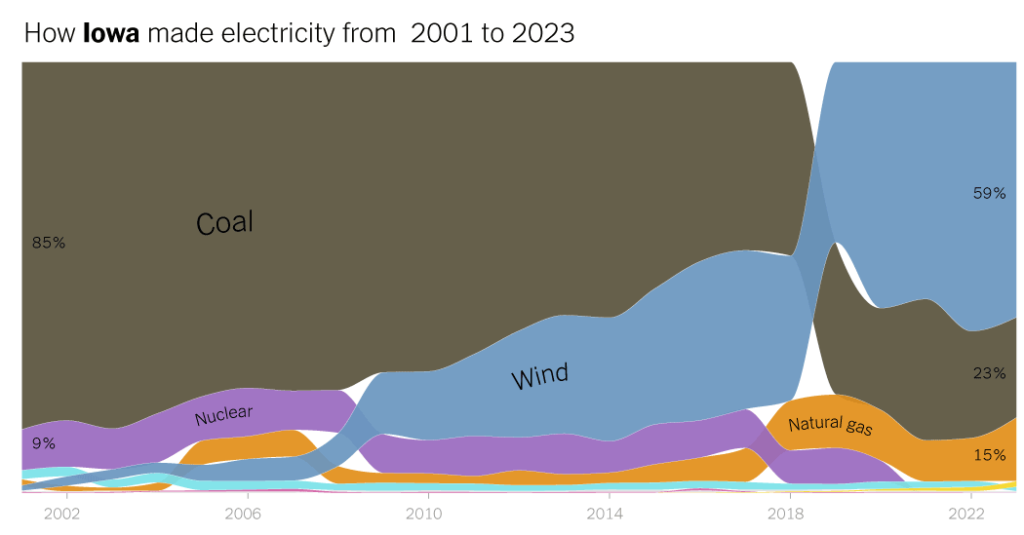
How Iowa made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Wind energy has taken off in Iowa over the previous decade, surpassing coal because the state’s prime supply of electrical energy in 2019. Wind generators offered simply 1 p.c of the electrical energy produced within the state in 2001 and almost 60 p.c final yr. Over the identical interval, coal-fired era considerably declined.
In absolute phrases, the state, one of many windiest in the country, was the second-largest producer of wind energy final yr, after Texas. However, as Iowa’s wind capability has grown, so has native opposition to new initiatives. In recent times, quite a lot of Iowa counties have paused the construction of new wind turbines and a few photo voltaic initiatives, too.
In 1983, Iowa grew to become the primary state within the nation to cross laws requiring utilities to get some quantity of electrical energy from renewable assets, however the state has not up to date these requirements since. Iowa exports a few of its energy to close by states over the regional electrical grid. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Kansas made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Kansas, like many states throughout the Nice Plains, has seen important development in wind energy over the previous decade as builders put up hundreds of generators to seize the robust winds blowing throughout the open prairie. In 2019, wind surpassed coal to change into Kansas’s largest supply of electrical energy era and has remained the state’s prime energy producer since then.
Kansas produces extra energy than it consumes and sends a couple of quarter to different states by means of the regional grid. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Kentucky made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal nonetheless generates the vast majority of the electrical energy produced in Kentucky, a longtime coal mining state. However quite a lot of the state’s older, coal-fired energy crops have shut down or been transformed to burn pure fuel over the previous decade. Coal fueled 68 p.c of the facility produced within the state final yr, down from greater than 90 p.c throughout many of the 2000s and early 2010s.
How Louisiana made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel has lengthy offered the majority of electrical energy era in Louisiana, one of many prime gas-producing states within the nation. However as coal era declined in recent times, fuel additional expanded its share of the state’s electrical combine. Final yr, fuel accounted for 76 p.c of electrical energy made within the state, up from 46 p.c in 2001. Throughout that point, coal-fired era declined, dropping from its place because the second-largest supply of energy within the state to a distant third place.
Louisiana additionally imports some electrical energy from neighboring states. (Imports should not proven within the chart above.)
How Maine made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Many of the electrical energy generated in Maine final yr got here from renewable sources. Collectively, hydroelectric dams, wind generators, photo voltaic arrays and biomass crops, which burn wooden and different natural supplies, produced about 69 p.c of the state’s energy.
Nonetheless, the whole quantity of energy generated in Maine, notably from pure fuel and petroleum, has declined considerably over the past twenty years. The state now imports between 10 and 30 p.c of its electrical energy annually from different close by states and Canada. (Imports should not proven on the chart above.)
Maine has a goal of getting one hundred pc of its electrical energy from renewable sources by 2050.
How Maryland made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal produced the majority of Maryland’s energy by means of the early 2010s, however its position within the state’s electrical energy combine has declined considerably over the past decade. Coal fueled simply 5 p.c of electrical energy made within the state final yr, down from greater than 40 p.c a decade earlier (and a good larger share earlier than then). Nuclear energy grew to become the most important supply of electrical energy era in 2015 and rapidly rising pure fuel energy surpassed nuclear for the primary time final yr.
Whereas solar energy remains to be a small a part of the state’s era combine, it has grown quickly over the previous a number of years, beating out hydro because the state’s largest supply of renewable electrical energy. Maryland requires that fifty p.c of the electrical energy offered by utilities within the state come from renewable sources by 2030.
Maryland consumes extra energy than it generates and imports a major quantity of electrical energy from different Mid-Atlantic States by means of the regional grid. (Imports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Massachusetts made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel has expanded its share of electrical energy era in Massachusetts over the previous twenty years as different sources of energy have declined. Coal-fired era petered out within the state by 2018. And petroleum, which is generally used to satisfy peak electrical energy demand throughout the winter, now gives solely a small fraction of the facility it did twenty years in the past. The state’s solely nuclear plant, which was answerable for between 10 and 20 p.c of the state’s electrical energy era in earlier years, shut down permanently in 2019, partly due to competitors from cheaper pure fuel.
Solely solar energy has bucked the pattern: The quantity of electrical energy created from photo voltaic vitality, largely by means of small-scale rooftop panels, has grown considerably since 2013 and now gives almost 1 / 4 of the state’s energy. Nonetheless, Massachusetts makes much less energy as we speak in absolute phrases than it did twenty years in the past and now imports about half of its energy from different Northeastern states by means of the regional grid. (Imports should not proven within the chart above.)
Massachusetts lawmakers have sought to encourage the adoption of extra photo voltaic and wind energy. (The state’s first offshore wind undertaking started producing electricity this yr.) The state requires utilities to get 80 percent of the electricity they sell from renewable sources by 2050.
How Michigan made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was the highest supply of electrical energy produced in Michigan for many of the final twenty years, however coal-fired era declined steadily throughout the 2010s and 2020s as pure fuel energy expanded. After years of development, fuel grew to become the state’s prime supply of electrical energy for the primary time in 2020 and retook that prime slot in 2022 and 2023. Nuclear was the second largest supply of energy produced within the state final yr, with coal falling to 3rd place.
Nuclear vitality is the state’s largest supply of emissions-free energy. It fueled 23 p.c of the electrical energy produced within the state final yr. Wind energy generated a further 7 p.c, and photo voltaic delivered lower than 2 p.c. Michigan just lately set a goal to get one hundred pc of its electrical energy from zero-carbon vitality sources by 2040.
To shore up extra emissions-free energy, Michigan now desires to reopen a nuclear plant that shut down in 2022, with assist from a $1.5 billion mortgage from the Biden administration. If the plan goes by means of, it will be the primary shuttered nuclear plant to reopen in the US.
How Minnesota made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was the highest supply of electrical energy produced in Minnesota for years, however its era share has declined over the past twenty years and, in 2020, coal-fired energy era dropped beneath nuclear for the primary time. Wind energy, in the meantime, grew from 2 p.c of the state’s complete era in 2001 to 25 p.c in 2023. Wind grew to become the state’s prime energy producer final yr.
Emissions-free vitality sources, together with wind, photo voltaic and nuclear energy, now present greater than 50 p.c of the facility produced in Minnesota. State regulation requires electrical utilities to generate or procure one hundred pc of their electrical energy from carbon-free sources by 2040. Minnesota additionally imports some energy from different states by means of the shared regional grid. (Imports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Mississippi made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel powered greater than three-quarters of the electrical energy generated in Mississippi final yr. Coal, as soon as the state’s prime supply of electrical energy, has declined considerably over the previous decade as pure fuel costs have fallen. Coal offered 36 p.c of the electrical energy produced within the state in 2001, however simply 5 p.c in 2023.
Mississippi produces extra energy than it makes use of and exports the excess to different states. (Exports should not proven on the charts above.)
How Missouri made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Missouri’s electrical energy era combine has been dominated by coal for greater than twenty years. Nonetheless, coal-fired energy declined to 59 p.c of all electrical energy generated within the state in 2023 from 82 p.c in 2001 as older coal crops went offline or switched to pure fuel. Fuel- and wind-powered era have made positive aspects over the previous decade, however, regardless of a dip in 2021, nuclear stays the state’s second largest supply of energy.
Missouri usually makes use of extra electrical energy than it generates in-state and pulls energy from different states by means of regional grids. (Electrical energy imports should not proven on the charts above.)
How Montana made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal has been the highest supply of electrical energy produced in Montana for many of the previous twenty years, however its share of the state’s era combine has declined as wind energy has grown and older coal-fired energy crops have been retired. Hydro, lengthy the state’s second-largest supply of electrical energy, briefly surpassed coal as the highest power-producer in 2020, however hydroelectric era dropped significantly by 2023 amid drought circumstances.
Montanans solely use about two-thirds of the electrical energy produced within the state. A lot of the remainder is shipped to Washington and Oregon through interstate transmission strains. New transmission projects are in development that might develop how a lot Montana-generated electrical energy strikes to different states (and the opposite method round, when wanted).
How Nebraska made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal has been the highest supply of electrical energy produced in Nebraska for greater than twenty years, however its era share has declined in recent times as wind energy has surged. The quantity of nuclear energy produced in Nebraska additionally declined after one of many state’s two nuclear crops, Fort Calhoun, completely shut down in 2016 for financial causes.
Nebraska, like many Nice Plains states, has wonderful wind assets, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, however as extra wind generators and photo voltaic farms have been constructed, local opposition to the projects has increased. A number of Nebraska counties just lately put in place moratoriums on new wind and photo voltaic initiatives, and others have instituted strict necessities for the place they are often constructed.
Nebraska produces extra energy than it consumes at house and sends the remainder to different states by means of long-distance transmission strains. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Nevada made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel surpassed coal as Nevada’s prime supply of energy era in 2005 and has been the state’s largest electrical energy provider since. Extra just lately, photo voltaic has surged to change into the state’s second-largest supply of electrical energy.
Within the meantime, coal energy has continued to say no. Lots of the state’s older, coal-fired energy crops have shuttered over the previous twenty years due to competition from cheaper natural gas and state laws that require renewable vitality improvement. Nevada’s two remaining coal crops are scheduled to be transformed to pure fuel by 2026.
Final yr, about 40 p.c of the facility produced within the state got here from renewable vitality. Massive-scale photo voltaic arrays and rooftop panels offered 26 p.c. Geothermal crops, which harvest warmth from deep beneath the Earth’s floor, provided a further 10 p.c. Many of the relaxation got here from hydro. (The Hoover Dam, one of many nation’s largest hydroelectric dams, sits on Nevada’s border with Arizona, offering energy to each states.)
The speedy development of solar energy in recent times has prompted the state to strengthen its goals for renewable energy. Nevada regulation now requires that fifty p.c of the electrical energy offered by utilities within the state come from renewable sources by 2030.
How New Hampshire made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
The majority of electrical energy generated in New Hampshire over the previous twenty years has come from the state’s solely nuclear reactor, Seabrook Station. Pure fuel has been the state’s second-largest supply of energy for the reason that early 2000s, when two new producing stations went on-line. The share of electrical energy provided by coal has declined over the previous twenty years, shrinking to about 1 p.c in 2023 from 25 p.c in 2001.
New Hampshire at present generates about 16 p.c of its electrical energy from renewable sources, largely hydro and biomass, a kind of vitality that comes from burning wooden and different natural matter. The state requires utilities to get 25 p.c of the facility they promote to clients from renewable sources by 2025, a goal they’ll fulfill by buying renewable vitality credit.
New Hampshire produces extra energy than it consumes and sends the surplus to different New England states and Canada. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How New Jersey made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Nuclear was the highest supply of electrical energy era in New Jersey till 2015, when pure fuel surpassed it for the primary time. Over the previous decade, pure fuel and nuclear vitality have produced virtually all the state’s electrical energy, however photo voltaic has made inroads, supplying 7 p.c of energy final yr.
In 2018, the state’s Oyster Creek nuclear plant, the oldest within the nation on the time, closed down, partly due to competitors from cheaper pure fuel. That very same yr, the New Jersey Legislature approved new subsidies to maintain the state’s remaining three nuclear crops worthwhile. The governor, Philip D. Murphy, stated the crops offered essential, emissions-free energy that may not contribute to local weather change and pointed to “the hundreds of jobs they help.”
New Jersey has a renewable energy standard that requires 35 p.c of the electrical energy offered within the state to return from renewable sources by 2025, with that requirement growing to 50 p.c by 2030. To assist attain these objectives, the state wants to build wind farms off its coast, the place there’s considerable wind power potential. However proposed initiatives have stirred up fierce local opposition.
The state consumes extra energy than it produces inside its borders and imports electrical energy from close by states by means of the regional grid. (Imports should not included on the chart above.)
How New Mexico made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was New Mexico’s major supply of electrical energy era for many of the final twenty years. However coal-fired energy has declined for the reason that 2000s in response to more durable air high quality laws, cheaper pure fuel and California’s determination in 2014 to cease buying electrical energy generated from coal in neighboring states. Over the previous decade, wind-powered era has surged in New Mexico, and, in 2022, wind surpassed coal as the highest supply of electrical energy produced within the state.
New Mexico has among the greatest wind, photo voltaic and geothermal vitality assets within the nation, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration. Final yr, the state produced greater than 46 p.c of its energy from renewable vitality, largely wind and photo voltaic. State regulation requires investor-owned utilities to get 50 p.c of the electrical energy they promote from renewable sources by 2030, and one hundred pc from a broader array of carbon-free sources by 2045.
The state already exports a major quantity of electrical energy to Arizona and California, however it might quickly change into a good larger energy provider. Final yr, officers broke ground on a major new transmission project that may ship renewable wind energy from central New Mexico to more-populated elements of the West. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How New York made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel and nuclear vitality have fueled the vast majority of New York’s electrical energy for the previous twenty years. However fuel has expanded its position within the state’s energy combine throughout that point, whereas nuclear era declined in recent times. The state shut down its controversial Indian Point nuclear plant in 2021, inflicting nuclear era to fall and greenhouse gas emissions to rise.
Final yr, about 32 p.c of the facility produced in New York got here from renewable sources, largely hydro. The state turned on its first offshore wind farm on the finish of the yr however has struggled to get different offshore wind initiatives off the bottom. The state’s ambitious climate law requires utilities to get 70 p.c of the electrical energy they promote from renewable sources by 2030 and to shift completely to carbon-free energy a decade later.
New York tends to eat extra electrical energy than it produces and at present imports energy from neighboring states and Canada. (Electrical energy imports should not included on the chart above.)
How North Carolina made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal-fired energy crops offered the vast majority of North Carolina’s electrical energy era throughout the 2000s , however 32 of the state’s coal-burning units have retired since 2010 and coal’s share within the state electrical energy combine has dwindled. Pure fuel, in the meantime, has surged to change into North Carolina’s prime supply of energy, producing greater than 40 p.c of the state’s electrical energy final yr.
North Carolina additionally will get almost a tenth of its energy from photo voltaic. The state’s distinctive implementation of a decades-old federal mandate, the Public Utility Regulatory Insurance policies Act of 1978, helped encourage the development of utility-scale solar projects, however the development of solar energy has slowed in recent years.
In 2021, a bipartisan invoice handed by state lawmakers required North Carolina’s largest utility, Duke Power, to attain a 70 percent reduction in carbon dioxide emissions from 2005 ranges by the top of the last decade. However this yr, Duke Power asked for more time to meet that deadline and for permission to construct a fleet of latest gas-burning energy crops.
How North Dakota made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
As in lots of Nice Plains states, wind energy has grown quickly in North Dakota. Final yr, wind generators generated 36 p.c of the state’s electrical energy, greater than twice as a lot as a decade earlier than. However coal nonetheless dominates the state’s electrical combine.
North Dakota has each substantial coal reserves and abundant wind. The state produces considerably extra electrical energy than is consumed inside its borders and sends about two-thirds to neighboring states and Canada by means of high-voltage transmission strains. (Exports should not included on the chart above.)
How Ohio made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was Ohio’s primary supply of energy for a lot of the final twenty years, however a increase in hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, introduced cheaper pure fuel within the 2010s and utilities shut down a number of massive coal crops. Fuel took over because the state’s prime supply of electrical energy in 2019 and now fuels almost 60 p.c of the state’s energy era.
Ohio produces a further 12 p.c of its electrical energy from two nuclear crops alongside Lake Erie, which have additionally confronted stiff price competitors from fuel. In 2019, Ohio lawmakers passed a bill that gave the state’s nuclear energy crops greater than $1 billion in subsidies to remain open, bailed out two coal crops and weakened the state’s renewable electrical energy necessities. The nuclear subsidies had been repealed in 2021 amid a significant public corruption scandal, however different elements of the regulation have remained in place.
Ohio will get a small portion of its energy from renewable sources as we speak: About 2 p.c from wind vitality and 1 p.c from photo voltaic. Multiple-fourth of Ohio counties have banned or restricted the construction of new wind or solar projects since 2021 when one other state regulation gave county officers decision-making energy over the place to find renewable vitality.
How Oklahoma made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
The vast majority of Oklahoma’s energy era has traditionally come from fossil fuels, however wind energy has surged within the state over the previous decade. Coal was the state’s prime energy producer within the 2000s, however pure fuel started competing for the highest slot within the late 2000s and early 2010s and coal energy declined sharply over the subsequent decade. Wind energy has grown rapidly within the meantime, briefly turning into the state’s largest energy producer in 2022 earlier than dropping beneath fuel once more final yr.
Oklahoma was the third-largest producer of wind energy within the nation final yr, behind Texas and Iowa. The state generates extra electrical energy than it consumes and sends its additional energy to different states over the regional grid. (Exports should not included on the chart above.)
How Oregon made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Many of the electrical energy produced in Oregon in any given yr comes from hydroelectric dams, however the actual quantity can fluctuate relying on precipitation. Energy from pure fuel usually will increase throughout drought years and reduces in years with ample rain and snow.
Over the previous decade, wind has grown to change into the third-largest supply of electrical energy generated within the state. In an effort to encourage extra non-hydroelectric renewable energy, Oregon requires its massive, investor-owned utilities to get 50 percent of the electricity they sell to customers from new renewable energy sources by 2040. Different utilities are topic to decrease requirements.
In most years, Oregon exports a few of its energy to close by states. (Exports should not included within the chart above.)
How Pennsylvania made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was Pennsylvania’s prime supply of electrical energy till 2014, however its position within the state’s energy combine has declined sharply since then as pure fuel has surged.
Fuel manufacturing from hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, unleashed a flood of low-cost pure fuel in Pennsylvania beginning within the 2000s. Because of this, electrical utilities started closing down older coal crops in favor of newer gas-powered generators.
Fuel is now placing stress on the state’s nuclear crops, too. After one of many state’s nuclear energy crops, Three Mile Island, shut down in 2019, pro-nuclear teams sought state subsidies to maintain the remaining reactors open, saying that the lack of this emissions-free electrical energy is bad news for climate change. Final yr, nuclear fueled 32 p.c of the state’s energy era, whereas different carbon-free sources provided lower than 4 p.c.
Pennsylvania is the nation’s third-largest producer of electrical energy, behind Texas and Florida, and the state is a significant provider of energy to the remainder of the Mid-Atlantic area. (Electrical energy exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Rhode Island made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Pure fuel dominates electrical energy era in Rhode Island, however photo voltaic vitality has grown rapidly in recent times. Photo voltaic provided 12 p.c of the state’s electrical energy final yr, up from lower than 1 p.c in 2017.
Rhode Island tightened its renewable vitality commonplace in 2022 and now requires state electrical energy suppliers to get one hundred pc of the facility they promote to shoppers from renewable sources by 2033. The state consumes extra electrical energy than it generates and imports additional energy by means of New England’s regional grid. (Imports should not included on the chart above.)
How South Carolina made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
The vast majority of the electrical energy generated in South Carolina has come from nuclear energy for greater than twenty years. However era from pure fuel has greater than doubled within the state over the previous decade as coal energy has declined. Fuel overtook coal in 2018 because the state’s second-largest energy producer.
In 2017, utilities in South Carolina abandoned plans to build two new nuclear reactors after main delays and billion-dollar price overruns. The state produced lower than 8 p.c of its energy from renewable sources final yr, largely photo voltaic and hydro.
South Carolina produces extra energy than it consumes and sends the excess to neighboring states. (Exports should not included on the chart above.)
How South Dakota made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Hydroelectric dams provided the majority of electrical energy era in South Dakota for a lot of the previous twenty years, however coal surpassed hydro because the state’s prime energy producer throughout three years — 2001, 2004 and 2008 — and, extra just lately, wind energy has taken over.
Coal’s share of the state era combine has declined considerably for the reason that 2010s. Wind, nonetheless, has surged. Wind vitality has been South Dakota’s prime supply of energy since 2021, supplying greater than half of the state’s electrical energy era final yr.
South Dakota makes way more energy as we speak than it did twenty years in the past and exports electrical energy throughout the Central and Western United States. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Tennessee made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was Tennessee’s prime supply of electrical energy era between 2001 and 2016, however its share of the state’s energy combine has declined considerably over the previous decade. In 2016, a brand new nuclear reactor was finally completed in Tennessee after a long time of delays. In 2017, coal-powered era dipped beneath nuclear for the primary time in almost twenty years. Extra just lately, rising pure fuel era has vied with coal because the state’s second largest energy producer.
Tennessee consumes extra energy than it produces and makes up the shortfall by importing electrical energy from close by states. (Imports should not included on the chart above.)
How Texas made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Texas produces extra electrical energy than another state, by a large margin, and its energy combine has lengthy been led by pure fuel. Coal-fired era within the state has declined over the previous decade as wind energy has elevated. In 2020, wind surpassed coal to change into the second-largest supply of electrical energy era in Texas.
The state is, by far, the nation’s largest producer of wind energy as we speak, with Iowa and Oklahoma in a distant second and third place. In recent times, solar energy has additionally surged within the state, rising from 1 p.c of the state’s electrical combine in 2019 to six p.c final yr.
Utilities and companies within the state have largely turned to wind and solar energy as a result of they’re so low-cost to construct, and never due to state mandates. Nonetheless, the state has cleared most of the obstacles to constructing new renewable initiatives and different vitality infrastructure, creating “an setting the place these items can thrive,” Dr. Lott of Columbia College stated.
However at the same time as energy era from renewable sources soars, in absolute phrases, Texas continues to burn extra pure fuel and extra coal than another state.
Not like most different states, Texas operates its personal energy grid, which is just minimally related to the nation’s different regional grids. Which means Texas is essentially dependent by itself assets to satisfy its electrical energy wants.
How Utah made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
The vast majority of electrical energy produced in Utah nonetheless comes from coal, however coal’s share of the state’s energy combine has declined over the past decade as pure fuel and photo voltaic era have elevated.
Photo voltaic is the most important renewable supply of energy within the state, offering 14 p.c of Utah’s electrical energy era final yr. Utah has a goal for utilities to generate or procure 20 p.c of the electrical energy they promote to clients from renewable sources by 2025.
The state produces extra vitality than it consumes and sends the excess to close by states, like California. (Exports should not included on the chart above.)
A minimum of one Utah energy plant is switching from burning coal to natural gas to adjust to California’s stricter environmental laws. However Utah lawmakers are taking a look at methods to keep the coal power plant running alongside the brand new fuel facility.
How Vermont made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Many of the electrical energy generated in Vermont got here from nuclear energy till 2014, when the state’s solely nuclear plant, Vermont Yankee, closed down. Since then, just about all the electrical energy produced within the state has come from renewable sources, together with hydropower, biomass, wind and photo voltaic.
However Vermont now generates a lot much less electrical energy, in complete, than it did earlier than the nuclear plant shut down and has to import a considerable quantity of energy from different New England states and Canada to fulfill demand. (Imports should not proven on the chart above.)
Vermont just lately strengthened its renewable vitality commonplace to require that 100 percent of electricity sold in the state come from renewable sources by 2035.
How Virginia made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was the highest supply of electrical energy produced in Virginia between 2001 and 2008, however its share has declined since then. By 2015, pure fuel had change into the state’s largest supply of electrical energy, a results of the nationwide increase in hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, which unleashed a wave of low-cost, plentiful fuel. Nuclear era has offered slightly greater than one-third of Virginia’s electrical energy, on common, over the previous twenty years.
In 2020, Virginia’s Democratic-led Legislature passed a clean energy law that established new vitality effectivity requirements, set a schedule for closing outdated fossil gasoline energy crops and required the state’s two greatest utilities get all of their electrical energy from carbon-free sources by 2050. However a brand new, Republican administration has pushed to revise that regulation and shift the state’s focus towards an “all of the above” energy strategy that features larger help for pure fuel energy.
The whole quantity of energy produced in Virginia has been rising, however the state can also be dealing with rising demand from power-hungry data centers. Dominion Power, the state’s largest electrical utility, has proposed meeting that demand with a mixture of new renewable energy and fuel era in a plan that might improve the corporate’s total emissions.
Virginia at present consumes extra electrical energy than it generates and will get extra energy from two regional grids that serve the state. (Imports should not included on the chart above.)
How Washington made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Washington is the nation’s largest producer of hydroelectric energy, which has dominated the state’s era combine for greater than twenty years. The quantity of energy produced by hydro fluctuates from yr to yr with adjustments in precipitation, and different sources — together with pure fuel, nuclear, wind and coal — make up virtually all the relaxation.
Washington produces extra electrical energy than it consumes and exports energy to Canada and different Western states. (Exports should not proven on the chart above.)
In 2019, the state required its electrical utilities to transition fully away from fossil fuels as a power source by 2045.
How West Virginia made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal nonetheless dominates West Virginia’s energy combine. It has provided greater than 85 p.c of the electrical energy produced within the state yearly for greater than twenty years. Whereas pure fuel and wind have elevated their era share over the previous decade, they nonetheless account for a comparatively small portion of the electrical energy produced within the state.
In 2015, West Virginia grew to become the primary state to repeal its renewable energy standard after years of lobbying by conservative teams. The regulation required utilities to get 25 p.c of their electrical energy from various and renewable vitality sources by 2025. Opponents of the usual stated it was hurting coal jobs and elevating electrical energy charges, whereas supporters stated it will assist to diversify the state’s electrical sector at a time when the nationwide coal market was in decline.
The whole quantity of energy generated by West Virginia has declined over the previous twenty years as coal energy has been squeezed by competition from cheaper regional sources and older coal-fired energy crops have retired. However the state nonetheless generates extra electrical energy than it consumes and provides a major quantity of energy to different Mid-Atlantic States by means of the shared regional grid. (Exports should not pictured within the chart above.)
How Wisconsin made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
Coal was lengthy Wisconsin’s prime supply of electrical energy era, however, after years of speedy development, pure fuel took over because the state’s largest energy producer in 2022. Wind and solar energy have grown rapidly within the state in recent times, however each sources stay comparatively small gamers in Wisconsin’s electrical energy combine.
In 2019, Gov. Tony Evers, a Democrat, set a aim for the state to shift to 100 percent carbon-free electricity by 2050 and created a brand new state workplace to guide the transition. However the proposal has confronted opposition from the Republican-led Legislature.
Wisconsin makes use of extra electrical energy than it generates in-state, so it imports extra energy from the regional electrical grid. (Imports should not proven on the chart above.)
How Wyoming made electrical energy
from 2001 to 2023
Share of energy produced from every vitality supply
The overwhelming majority of electrical energy generated in Wyoming nonetheless comes from coal, however wind energy has made inroads over the previous decade. Final yr, wind provided greater than a fifth of the electrical energy produced within the state.
Wyoming has been the nation’s prime coal-producing state for many years and the state can also be home to “some of the greatest wind resources in the nation,” in accordance with the U.S. Power Info Administration.
Due to its small inhabitants, Wyoming produces way more energy than it consumes and sends about 60 p.c out of state. A number of major transmission line projects are at present in improvement to maneuver extra of Wyoming’s ample wind energy to different Western states. (Exports should not pictured within the chart above.)
Information notes and methodology
Information comes from the U.S. Power Info Administration and displays internet electrical energy era between 2001 and 2023, damaged out by gasoline supply. The info contains utility-scale energy era and small-scale era from applied sciences like rooftop photo voltaic, in addition to industrial and business cogeneration. Information for 2023 is preliminary.
Cross-state imports and exports of electrical energy should not proven within the charts, however electrical energy routinely flows between states and most states belong partly or in complete to wider energy markets. Nonetheless, every state has the facility to form its power-generation combine by means of laws. How states generate electrical energy can also be influenced by the provision of native and regional vitality assets. For instance: Plentiful wind within the Midwest, plentiful sunshine within the Southwest, and native coal in West Virginia and Wyoming.
The charts don’t replicate era from pumped hydro or grid-scale battery storage as a result of charging and discharging should not reported individually by the E.I.A.